Vertical Centrifugal Pumps
Typhoon
The TYPHOON Vertical Centrifugal Pumps are high-efficiency pumps for fixed installation, with the pump immersed directly in the storage tank.
These pumps are used for rapid fluid draining, with flows ranging from 6 to 40m3/hour. The particular design of the semi-open impeller allows for continuous pumping even with dirty fluids, with an apparent viscosity of up to 500cps, and with small solid parts in suspension.
The TYPHOON are electric transmission pumps that, through a flexible coupling, transmit rotation to the shaft, and the impeller, thanks to the centrifugal effect, draws in through the central duct and releases through the peripheral tube.
OPERATING PRINCIPLE OF THE CENTRIFUGAL PUMP
The centrifugal pump is a type of hydraulic pump (or turbomachine) that processes the working fluid in a constant volume over time through always-open channels, typically with a stationary flow (hence, no internal valves are needed).
When the impeller (rotating part) is set in motion, it imparts rotation to the fluid (kinetic energy) and creates a suction in the intake duct. This suction, along with the force of atmospheric pressure, draws the liquid into the centrifugal pump.
Inside the pump, the fluid follows a path from the center of the impeller to its periphery, driven by centrifugal forces. It passes through channels with increasing cross-sections formed by curved blades. During this passage, part of the kinetic energy is converted into pressure energy.
Upon exiting the impeller, the fluid enters the volute, which also has an increasing cross-section. Here, the remaining kinetic energy is converted into pressure energy, increasing the pump’s head (or pressure capability). The more pressure energy transferred to the fluid, the higher the pump’s head, and the farther the working fluid can be sent.
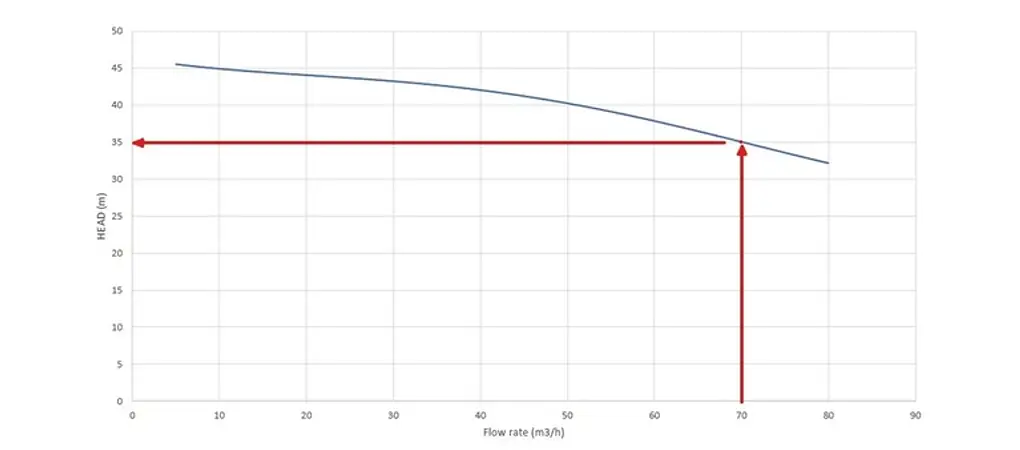
The operating range of a centrifugal pump is strictly limited to its characteristic curve. This curve defines the relationship between the head, flow rate, and power consumption under various operating conditions.
CHARACTERISTICS OF THE CENTRIFUGAL PUMP
Each centrifugal pump has its own characteristic curve, which is the graphical representation of the pump’s performance.
- On the x-axis (horizontal axis) is the flow rate Q, usually in m3/h. It indicates the amount of fluid that passes through each section of the centrifugal pump over a defined period. This amount depends on the pump’s dimensional characteristics, the motor’s speed (i.e., the rotation speed of the impeller), and the fluid’s characteristics (density and viscosity depending on temperature). The flow rate influences all the performances of the centrifugal pump and is the first technical parameter to consider.
- On the y-axis (vertical axis) is the head H, usually in meters. It is calculated from the pressure difference between the outlet and the inlet of the centrifugal pump and represents how far the fluid can be pushed if it encounters resistance along its path, such as height, curves, or valves.
Let’s define:
ΔZ as the height difference between the lower basin A and the upper basin B;
PA and PB as the pressures acting on the free surface of the upper basin A and the upper basin B respectively;
γ as the specific weight of the fluid (= fluid density*gravity acceleration g);
ΣY as the sum of distributed and localized losses inside the system.
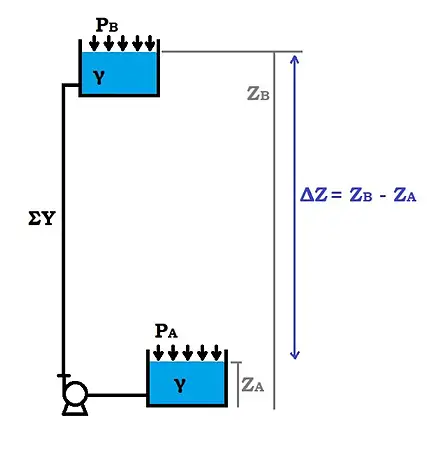
In ideal conditions, with perfectly smooth conduits, no curves, valves, or filters, thus 𝛴𝑌 = 0 and with 𝑃𝐴 = 𝑃𝐵 = ambient pressure, we would have 𝐻 = ΔZ, so the centrifugal pump imparts all its energy to overcome only the height.
In reality, the pump must overcome more than just the height difference as ideal conditions can never be achieved. Therefore, the head that needs to be reached is
H = ΔZ + (PB – PA)γ + Σ Y
Once the dimensions of the centrifugal pump (impeller and volute) and the rotation speed of the impeller (given by the motor’s RPM) are established, the characteristic curve is unique and typical for each pump.
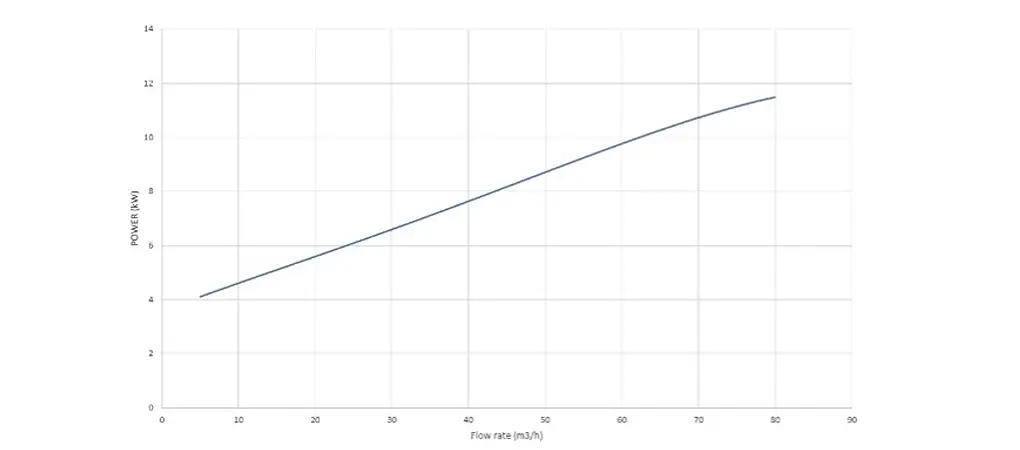
Knowing the specific weight of the fluid γ, it’s also possible to calculate the theoretical power 𝑾, in Watts, required to move it:
𝑊 = 𝛾 ⋅ 𝑄 ⋅ 𝐻
The actual power 𝑾𝒂 absorbed by the motor is slightly greater as it’s necessary to consider that there will always be losses due to friction and fluid dynamics within the pump itself, which are taken into account in the efficiency η. The power curve, always as a function of the flow rate Q, refers to the following formula
𝑊𝑎 = 𝑊/𝜂
It’s intuitive to understand that as the flow rate increases, the required power will also increase, as shown in the graph below.
CHOOSING A CENTRIFUGAL PUMP
The centrifugal pump is suitable for applications where it is required to transport a liquid quickly and continuously. However, before choosing it, it’s essential to evaluate all the operating conditions:
- Processed Fluid: A centrifugal pump is a high-performance but delicate machine. Therefore, the working liquid should have low to medium viscosity and a specific weight up to 1.9 kg/L. Higher values would excessively strain the mechanical parts and the impeller, and the operation of the motor would be compromised due to out-of-range absorptions. Despite the open impeller, which allows the passage of dirty liquids, it’s not advisable to suction liquids with long solid particles and a diameter larger than one millimeter. Using a centrifugal pump for overly corrosive or very dirty fluids risks damaging the impeller or mechanical seals.
- Temperature: Fluimac centrifugal pumps can be used in a range between -5°C and +65°C if made of polypropylene, otherwise between -20°C and +95°C if the centrifugal pump is made of PVDF. It’s important that the fluid always remains in a liquid state.
- Working Conditions: Each centrifugal pump is associated with a specific characteristic curve that shows the head [m] the machine can reach given a certain flow rate [m3/h]. Knowing the conditions of your system before choosing a centrifugal pump prevents the risk of inadequate performance and damage to the system and the machine.
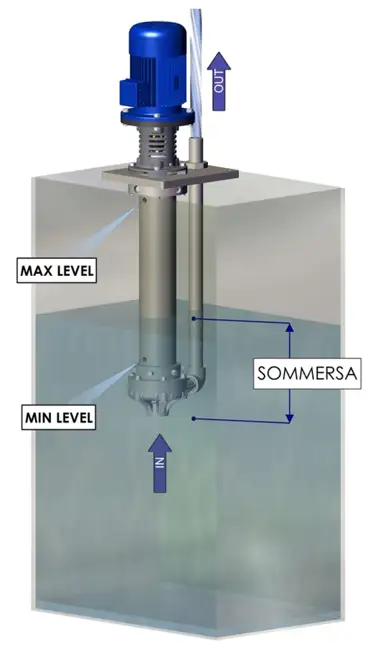
- Configuration: Fluimac offers both horizontal and vertical centrifugal pumps. The former are placed externally to the extraction tank, below the free level of the fluid, with the axis parallel to the ground; the latter are partially submerged in the fluid and positioned with a vertical axis relative to the ground.
- Motor Power Supply: Fluimac centrifugal pumps are designed primarily for electric motor operation, but configurations with pneumatic motors are possible. The system must be suitable and sized to ensure continuous power supply.
HOW OUR VERTICAL CENTRIFUGAL PUMP TYPHOON IS MADE
The centrifugal pump is a hydraulic turbomachine capable of processing the fluid by the work done due to centrifugal effect through fixed and rotating channels always open, without modifying the compressibility of the fluid itself. Hence the name centrifugal pump. The mechanical movement imparted by the motor to the impeller provides kinetic energy to the flow (acceleration in the radial direction) which is transformed into pressure energy in the subsequent diverging channels.
The main components of a vertical centrifugal pump are:
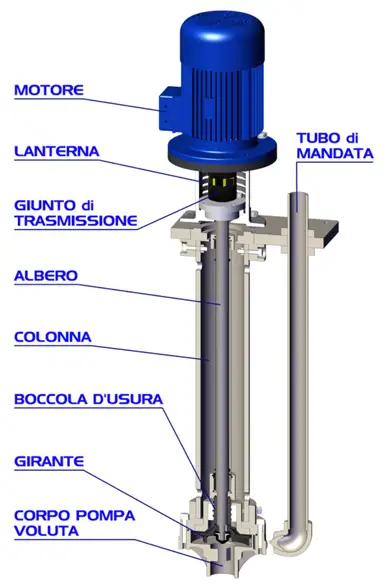
- The impeller is the main component of the centrifugal pump and the moving part with which the fluid exchanges energy. Made of plastic material reinforced with fibers (PP + FRP or PVDF + CF depending on the use of the centrifugal pump and the processed fluid), it consists of a series of curved blades that form increasingly larger channels as the radius increases. The open impeller allows the passage of slightly dirty liquids, while the processing of fluids with viscosities up to 500 CPS or specific weights up to 1.9 kg/L is guaranteed by the solid and concentric movement of the impeller relative to the motor, connected via a shaft and a transmission coupling.
It is possible to achieve different volumetric flows [m3/h] and heads [m] by controlling the diameter, curvature, height, and number of blades of the impeller. For each impeller, there will be a characteristic curve of the centrifugal pump, i.e., what head can be achieved given a certain flow rate, the operating range, and the working point.
- The pump body or volute, snail-shaped, with an increasing section in the direction of motion, allows the axial vertical suction of the fluid and radial delivery to the side, conveyed upwards through a discharge pipe. In addition to directing the flow, it is also fundamental for the performance of the centrifugal pump: the increasing area appropriately slows down the fluid, thus the kinetic energy is transformed into pressure energy.
- The wear bushing is the component that works by friction, thus subjected to greater wear. It keeps the shaft in a perfectly concentric position relative to the motor, which otherwise would rotate eccentrically due to the forces acting on the impeller. It consists of a rotating part integral with the impeller and a fixed part locked relative to the static components of the centrifugal pump. Normally a centrifugal pump reaches rotational speeds of about 3000 rpm, so it reaches very high temperatures in a very short time. It is essential that the bushing is always cooled (by the working liquid itself) and that the centrifugal pump is never operated dry, otherwise, there is a risk of melting the fixed components. The bushing is made of silicon carbide and Teflon, which guarantee less wear, greater mechanical and chemical resistance, and better withstand thermal shocks, allowing it to work at higher temperatures.
- The lantern contains the motion transmission elements: shaft and bearing connected to the motor via the transmission coupling. It must ensure perfect concentricity between fixed and rotating parts. To it is connected the covering column, which will come into contact with the fluid, via a support plate. The overall structure must be as solid and stable as possible to minimize vibrations that would be transmitted along the entire length of the vertical centrifugal pump.
- The motor is the part that transmits motion. In most cases, it is a 2-pole electric motor (about 3000 rpm). Depending on the number of revolutions, different characteristic curves of the centrifugal pump can be obtained.
The motor is the part that transmits motion. In most cases, it is a 2-pole electric motor (about 3000 rpm). Depending on the number of revolutions, different characteristic curves of the centrifugal pump can be obtained.
- Vertical centrifugal pumps maintain rotation concentricity through a wear bushing placed just above the impeller and must always be cooled. We have designed them so that this task is always performed by the working fluid, without the use of additional means, but it is important to remember that the vertical centrifugal pump should only be started when submerged at least up to the minimum level, never dry, to prevent the melting of fixed components.
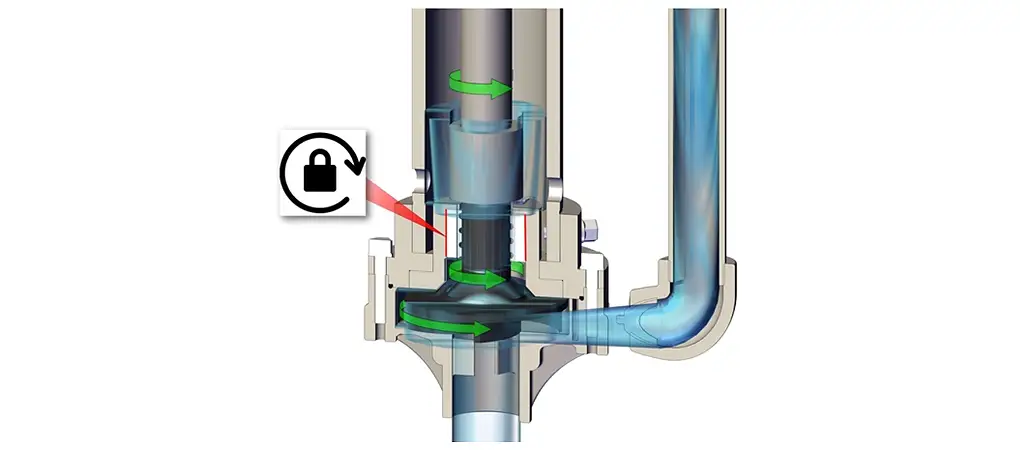
- Vertical centrifugal pumps are ideal when a continuous flow is required, but due to the high speeds and forces involved, it is preferable to avoid fluids rich in solid particles or highly corrosive, as they could damage the impeller and block the flow channels.
- It is possible to handle fluids with viscosities up to 500 CPS or specific weights up to 1.9 kg/L by increasing the power of the motor. At the same number of revolutions [rpm], increasing the motor power does not affect the flow rate and head of the centrifugal pump but compensates for the increased effort due to heavier liquids.
- A centrifugal pump is a very efficient but delicate machine. Knowledge of the plant and working fluid characteristics is necessary to choose the appropriate machine.
- Due to their operating principle, centrifugal pumps create a suction vacuum. If the absolute pressure at the impeller inlet is lower than the vapor pressure of the working fluid, cavitation may occur (formation of bubbles of evaporated liquid and implosion on the impeller). Vertical centrifugal pumps by Fluimac must always be installed under a head, partially submerged. However, it is possible to control the maximum suction height through NPSH (Net Positive Suction Head) curves: The pump’s NPSH (available) must always be greater than the NPSH required by the system, considering the geodetic height (height difference between the downstream and upstream tanks through which the fluid is moved), the pressure losses between these two sections, and the pressure difference between the free surface pressure of the downstream tank and the vapor pressure of the liquid.
- In addition to the suction conditions, it is essential to know the characteristics of the discharge pipes because they influence the calculation of head. Before choosing the vertical centrifugal pump, it is necessary to know the head required by the system: at the geodetic height (height difference between the downstream and upstream tanks through which the fluid is moved), all the losses in the system due to friction and local factors need to be added. We can divide the losses into two types: distributed and localized. The first type depends on the flow of the fluid in the pipes, and knowledge of the dimensions and conditions of the pipes is required, while the second type depends on factors located in the system, such as bends, valves, or filters.
- Finally, knowledge of the working fluid is required. Viscosity and density also affect the calculation of pressure losses and the choice of motor power.
Ask for advice
Do you need support in choosing the centrifugal pump most in line with your specific fluid handling needs?
Fill out the form below and you will be contacted by our staff.
The best solutions, certified








